Unveiling the intricacies of circles, unit 10 test circles answer key delves into the captivating world of geometry, where the beauty of circles unfolds. This comprehensive guide empowers students with a profound understanding of circle properties, measurements, and their multifaceted applications.
Through engaging explanations, insightful examples, and thought-provoking exercises, this answer key illuminates the fundamental concepts of circles, empowering learners to conquer geometry challenges with confidence and precision.
Circle Properties: Unit 10 Test Circles Answer Key

A circle is a two-dimensional figure that consists of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is called the radius.
Circles have several key properties:
- They are symmetrical about their center.
- They have a constant radius.
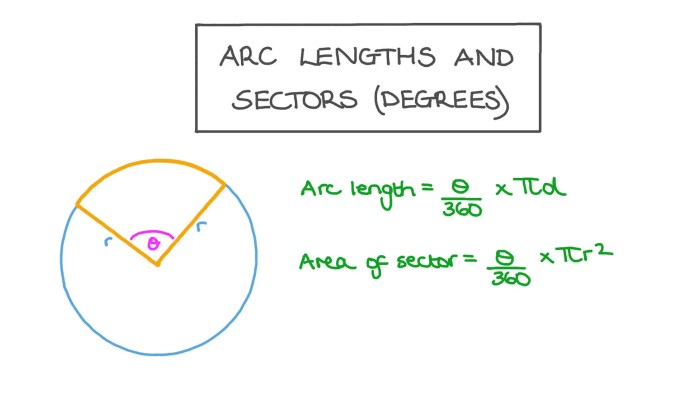
- They have a circumference that is equal to 2πr, where r is the radius.
- They have an area that is equal to πr², where r is the radius.
Circles are found in many real-world applications, such as:
- Wheels
- Gears
- Clocks
- Coins
- Planets
Relationship Between Radius and Diameter
The diameter of a circle is the distance across the circle through the center. The diameter is twice the radius, or d = 2r.
This relationship can be used to find the radius or diameter of a circle if you know the other measurement.
Circle Measurements
Circles are geometric shapes defined by a fixed point (center) and a constant distance (radius) from the center to any point on the circle’s boundary. Measuring circles involves determining their circumference (perimeter) and area.
Calculating Circumference
The circumference of a circle is the length of its boundary. It is calculated using the formula:
C = 2πr
where:
- C represents the circumference
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the radius of the circle
Calculating Area, Unit 10 test circles answer key
The area of a circle is the amount of space enclosed within its boundary. It is calculated using the formula:
A = πr2
where:
- A represents the area
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the radius of the circle
Practice Problems
1. Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
2. Calculate the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 m.
Circle Theorems
Circle theorems establish fundamental relationships between various elements within a circle. These theorems provide valuable insights into the properties and measurements of circles.
Pythagorean Theorem in Relation to Circles
The Pythagorean Theorem, commonly used in right triangles, can be extended to circles through the concept of secant and tangent lines. When a secant line intersects a circle, forming two tangent lines from an external point, the square of the length of the secant line segment outside the circle is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two tangent line segments.
$$(AB)^2 = (AC)^2 + (BC)^2$$
Inscribed Angle Theorem
The Inscribed Angle Theorem states that the measure of an inscribed angle (an angle whose vertex lies on the circle and whose sides intersect the circle) is half the measure of its intercepted arc. This theorem has practical applications in geometry, such as finding the measure of unknown angles in cyclic quadrilaterals and determining the length of arcs.
Similar Circles
Similar circles are circles that have the same shape but different sizes. They share the same center and are scaled versions of each other. The ratio of their radii and circumferences is constant, making it possible to determine unknown measurements based on known values.
Circle Constructions
Circle constructions involve creating a circle with specified properties, such as radius or diameter. Understanding these constructions is essential for various applications in geometry, engineering, and design.
Constructing a Circle Given Its Radius
To construct a circle given its radius, follow these steps:
- Draw a straight line segment and mark a point on it as the center of the circle.
- Set the compass to the length of the given radius.
- Place the compass point on the center point and draw an arc intersecting the line segment.
- Keep the compass point on the center point and draw another arc from the other end of the line segment, intersecting the first arc.
- The intersection points determine the endpoints of the circle’s diameter.
Constructing a Circle Given Its Diameter
To construct a circle given its diameter, follow these steps:
- Draw a straight line segment of the given diameter length.
- Mark the midpoint of the line segment as the center of the circle.
- Set the compass to half the length of the diameter.
- Place the compass point on the center point and draw a circle.
Using Technology in Circle Constructions
Technology can assist in circle constructions using software or online tools. These tools provide precise measurements, automated steps, and various options for circle creation. However, understanding the manual construction methods is crucial for comprehension and problem-solving.
Circle Applications
Circles find widespread applications in various fields, including engineering, architecture, design, navigation, astronomy, and sports. Their unique geometric properties make them essential for solving real-world problems and creating aesthetically pleasing designs.
Engineering
- Bridges and Buildings:Arches and domes, commonly used in bridges and buildings, utilize the structural strength of circles to distribute weight evenly and withstand external forces.
- Gears and Pulleys:Circular gears and pulleys are fundamental components in machines, allowing for efficient transmission of motion and power.
- Pipelines and Storage Tanks:Cylindrical pipes and spherical tanks are widely used for transporting and storing fluids, gases, and other materials.
Architecture
- Columns and Arches:Circular columns and arches are prominent architectural elements, providing both structural support and aesthetic appeal.
- Domes and Rotundas:Domes and rotundas, characterized by their circular shape, create expansive and visually stunning spaces in buildings.
- Windows and Doors:Circular windows and doors add a unique and elegant touch to architectural designs, often used to enhance natural lighting and ventilation.
Design
- Logos and Branding:Circles are commonly used in logos and branding, conveying concepts such as unity, completeness, and harmony.
- Product Design:Circular shapes are prevalent in product design, from furniture to electronics, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
- Fashion and Jewelry:Circular motifs are frequently found in fashion and jewelry, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication to designs.
Navigation
Circles play a crucial role in navigation, providing a means to determine direction and measure distances.
- Compasses:Compasses utilize a circular dial with a rotating needle to indicate magnetic north, aiding in navigation.
- Maps and Globes:Maps and globes often incorporate circles to represent geographical features such as latitudes and longitudes.
- Sailing and Air Navigation:Sailors and pilots use circular instruments like protractors and compasses to calculate courses and determine positions.
Astronomy
Circles are fundamental in astronomy, describing the motions and characteristics of celestial bodies.
- Orbits:Planets and moons orbit stars and planets in circular or elliptical paths.
- Stars and Galaxies:Stars and galaxies often exhibit circular or spiral shapes, providing insights into their formation and evolution.
- Eclipses:Solar and lunar eclipses occur when the Earth, Moon, and Sun align in a circular configuration.
Sports
- Balls and Rings:Balls used in sports like basketball, soccer, and tennis are spherical, allowing for smooth movement and controlled trajectory.
- Tracks and Arenas:Running tracks and sports arenas often incorporate circular shapes to define boundaries and provide a consistent playing surface.
- Scoring and Measurement:Circular targets are used in archery and shooting sports to determine accuracy and score points.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Circles have held cultural and historical significance throughout human history, representing concepts of unity, completeness, and infinity.
- Religious Symbols:Circles are often found in religious symbols, representing the divine, the universe, and the cycle of life.
- Art and Architecture:Circular motifs are prevalent in art and architecture across cultures, symbolizing harmony, balance, and perfection.
- Timekeeping:Clocks and sundials utilize circular dials to measure and display time.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the formula for finding the circumference of a circle?
C = 2πr
How do you prove the Pythagorean Theorem in relation to circles?
In a right triangle inscribed in a circle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
What is the Inscribed Angle Theorem?
The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc.