Embarking on a journey to decipher the intricacies of topographic maps, we present the topographic map practice sheet answer key, an invaluable guide to unlocking the secrets hidden within these maps. Delve into the realm of contour lines, elevation, and map symbolism, and emerge as a master of map interpretation.
Through this comprehensive guide, we unravel the techniques for determining elevation, measuring distances, and identifying landforms. The significance of map symbols and the art of interpreting colors and patterns will be illuminated, empowering you to navigate the complexities of topographic maps with ease.
Topographic Map Features: Topographic Map Practice Sheet Answer Key
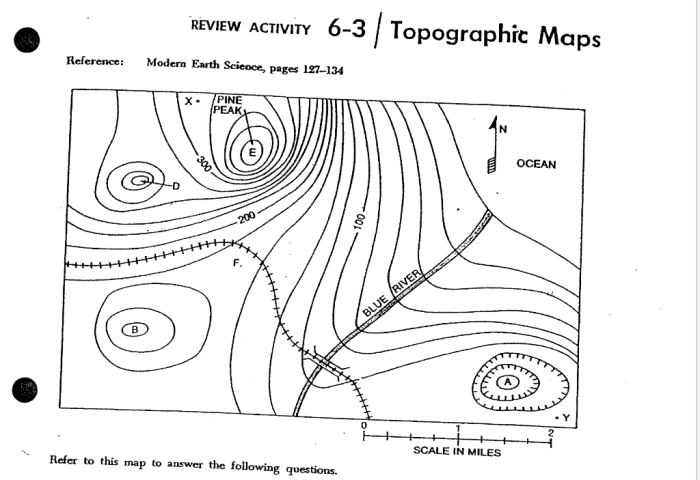
Topographic maps are essential tools for understanding the terrain and navigating the landscape. They provide a wealth of information about the elevation, shape, and features of the land. Here are some key topographic map features:
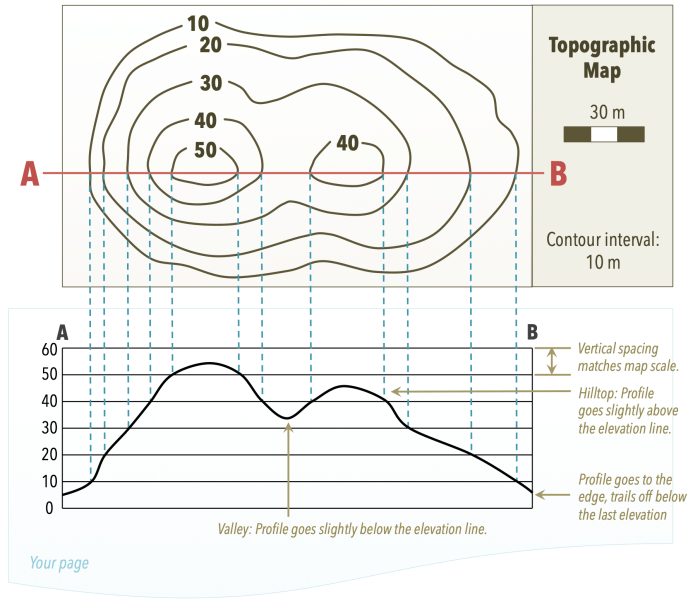
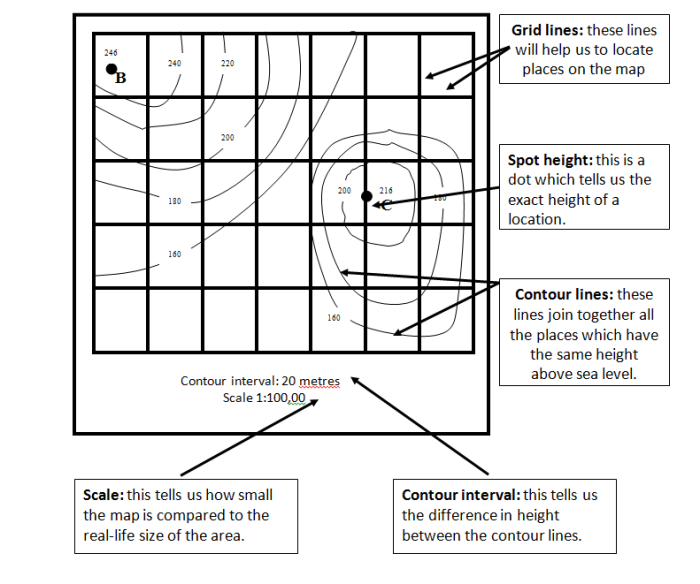
Contour Lines:Contour lines are the most important feature on a topographic map. They connect points of equal elevation, forming lines that trace the shape of the land. The closer together the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
Elevation:Elevation is the height of a point above sea level. On topographic maps, elevation is represented by contour lines. The elevation of a point can be determined by interpolating between the contour lines.
Contour Intervals:The contour interval is the vertical distance between adjacent contour lines. It is typically constant for a given map, and it determines the level of detail shown on the map.
Index Contours:Index contours are thicker contour lines that are labeled with their elevation. They help to identify the elevation of specific points on the map.
Hachures:Hachures are short, dashed lines that are used to indicate the direction of slope. They point downhill and are perpendicular to the contour lines.
Map Analysis Techniques
Topographic maps can be used to analyze the terrain and make informed decisions about navigation, land use, and other activities. Here are some common map analysis techniques:
Determining Elevation:The elevation of a point can be determined by interpolating between the contour lines. To do this, find the two contour lines that are closest to the point, and then estimate the elevation of the point based on its position between the two lines.
Measuring Distances:Distances can be measured on topographic maps using a scale or a measuring wheel. The scale is a graphic representation of the relationship between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
Calculating Slopes:The slope of a hill can be calculated using the contour lines. The steeper the slope, the closer together the contour lines will be. The slope can be expressed as a percentage or as an angle.
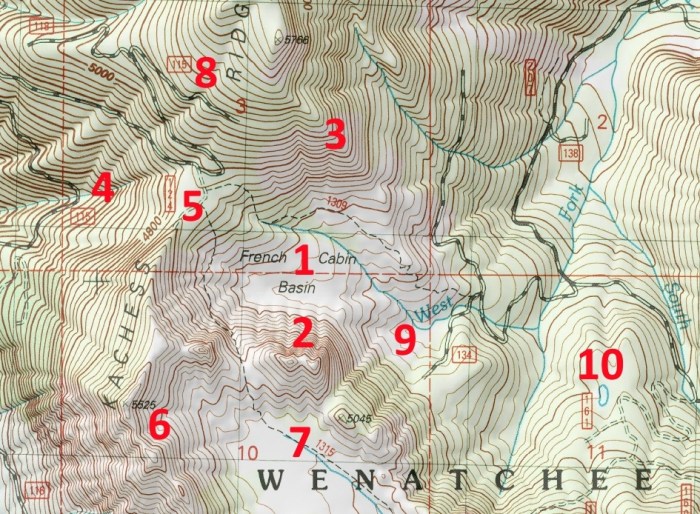
Identifying Landforms:Topographic maps can be used to identify landforms such as hills, valleys, and ridges. Hills are areas of high elevation, while valleys are areas of low elevation. Ridges are lines of high elevation that connect hills.
Map Symbolism and Interpretation, Topographic map practice sheet answer key
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols to represent different features on the landscape. These symbols are standardized and are the same on all topographic maps. Here are some common map symbols:
Roads:Roads are represented by lines. The width of the line indicates the type of road. For example, a wide line represents a major highway, while a narrow line represents a dirt road.
Buildings:Buildings are represented by rectangles. The size and shape of the rectangle indicates the size and shape of the building.
Water Bodies:Water bodies are represented by blue areas. The shape of the blue area indicates the shape of the water body. For example, a blue circle represents a lake, while a blue line represents a river.
Legend:The legend is a key that explains the meaning of the symbols used on the map. The legend is typically located in the corner of the map.
Colors and Patterns:Colors and patterns are used on topographic maps to convey information about the terrain. For example, green areas indicate forested areas, while brown areas indicate mountainous areas.
Topographic Map Applications
Topographic maps have a wide range of applications in fields such as hiking, navigation, and land planning. Here are some examples of how topographic maps are used:
Hiking:Topographic maps are essential for hikers. They can be used to plan routes, identify landmarks, and avoid dangerous areas. Topographic maps can also be used to estimate the distance and elevation gain of a hike.
Navigation:Topographic maps can be used for navigation in both urban and rural areas. They can be used to find roads, trails, and other landmarks. Topographic maps can also be used to determine the best route to take between two points.
Land Planning:Topographic maps are used by land planners to make informed decisions about land use. They can be used to identify areas that are suitable for development, agriculture, or conservation.
Other Applications:Topographic maps are also used in a variety of other applications, such as geology, forestry, and water resources management.
Popular Questions
What is the purpose of a topographic map?
Topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, depicting elevation, landforms, and other physical features.
How do I determine the elevation of a point on a topographic map?
Elevation can be determined by interpolating between the contour lines that surround the point of interest.
What do the different colors and patterns on a topographic map represent?
Colors and patterns are used to convey information about land cover, vegetation, and other features.