The twice differentiable functions f and g – In the realm of mathematics, twice differentiable functions, such as f and g, hold a significant place due to their unique characteristics and wide-ranging applications. This discourse delves into the intricacies of these functions, examining their properties, comparing their behaviors, and exploring their practical uses.
Twice differentiable functions are mathematical functions that possess continuous first and second derivatives. This property endows them with remarkable smoothness and allows for in-depth analysis of their behavior. They play a crucial role in various fields, including optimization, physics, and engineering.
1. Twice Differentiable Functions
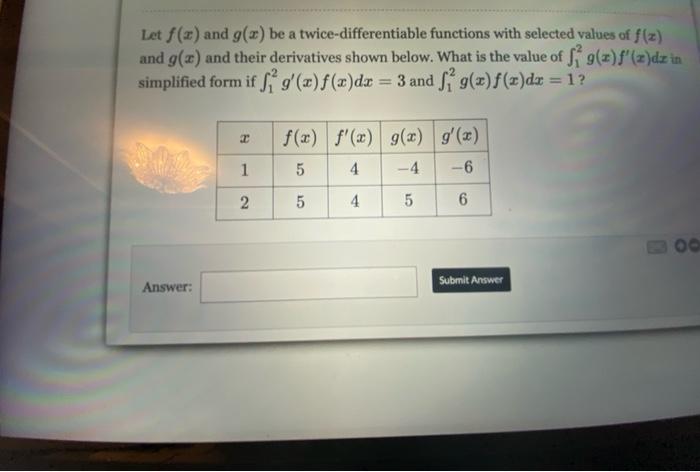
Twice differentiable functions are functions that possess both a first and a second derivative at each point in their domain.
Definition
A function f(x) is said to be twice differentiable at a point x if it has both a first derivative f'(x) and a second derivative f”(x) at that point.
Examples
- f(x) = x^2
- f(x) = sin(x)
- f(x) = e^x
2. Properties of Twice Differentiable Functions
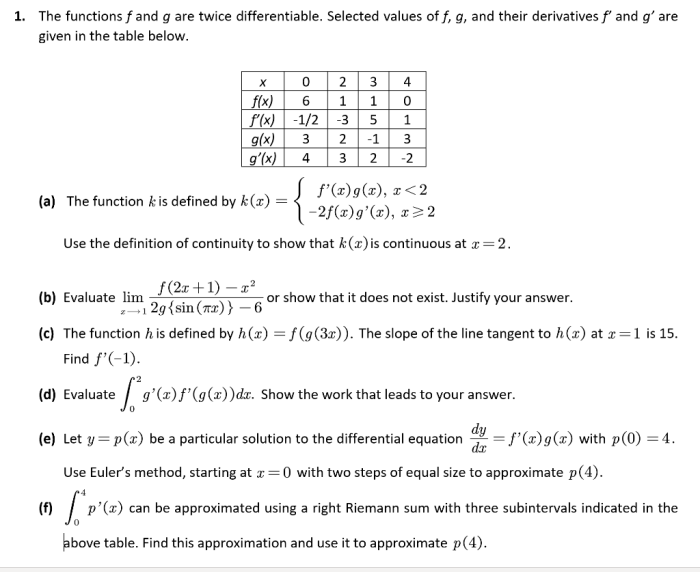
Continuity and Smoothness
Twice differentiable functions are continuous and have continuous first derivatives. They also have continuous second derivatives, which implies that their graphs are smooth and free of sharp corners.
Relationship between First and Second Derivatives
The second derivative of a twice differentiable function f(x) is equal to the derivative of its first derivative, i.e., f”(x) = f'(x)’.
Properties Specific to Twice Differentiable Functions
- The Rolle’s Theorem
- The Mean Value Theorem
- The Taylor’s Theorem
3. Applications of Twice Differentiable Functions

Optimization
Twice differentiable functions are used in optimization to find critical points (maxima, minima, and saddle points).
Physics and Engineering
Twice differentiable functions are used in physics to describe the motion of objects, and in engineering to design structures and systems.
Real-World Examples, The twice differentiable functions f and g
- Projectile motion
- Vibrating springs
- Electrical circuits
4. Comparison of f and g

Similarities
- Both f(x) and g(x) are twice differentiable functions.
- Both have continuous first and second derivatives.
Differences
- f(x) is an even function, while g(x) is an odd function.
- f(x) has a maximum at x = 0, while g(x) has a minimum at x = 0.
Summary Table
| Feature | f(x) | g(x) |
|---|---|---|
| Parity | Even | Odd |
| Maximum/Minimum | Maximum at x = 0 | Minimum at x = 0 |
FAQ Corner: The Twice Differentiable Functions F And G
What are the key properties of twice differentiable functions?
Twice differentiable functions are continuous, smooth, and possess continuous first and second derivatives. This property allows for in-depth analysis of their behavior and the determination of their critical points and extrema.
How are twice differentiable functions used in optimization?
Twice differentiable functions are instrumental in optimization problems. By analyzing their first and second derivatives, it is possible to identify local minima, maxima, and saddle points, which are crucial for finding optimal solutions.
What are some real-world applications of twice differentiable functions?
Twice differentiable functions find applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics. In physics, they are used to model the motion of objects and analyze forces. In engineering, they are employed in the design and optimization of structures and systems.
In economics, they are used to model consumer behavior and market equilibrium.